An Excerpt From ExerciseNatural.com
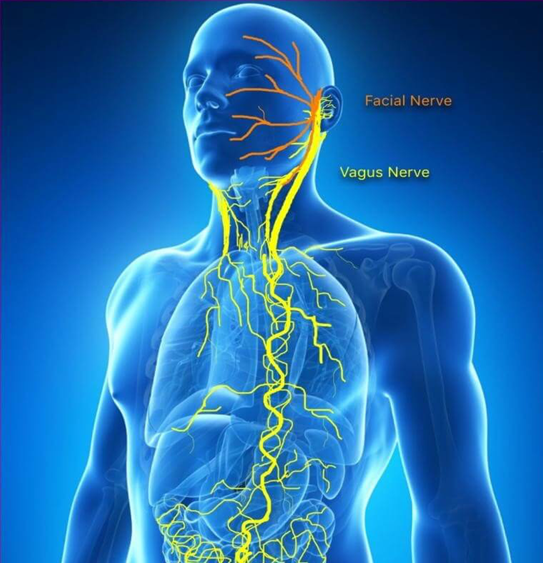
The vagus nerve is widely regarded as the primary means of communication between the GI tract and the brain. It controls the gut-brain link which sends signals in both directions. The vagus nerve is the longest nerve in the body, it extends from the base of the brain through the neck, branches off in the chest, and continues all the way down to the abdomen, touching the heart and nearly all major organs along the way.
Risks
Poor vagal functioning can result in stagnation and bacterial overgrowth in the GI tract. Which demonstrates the interconnectedness of everything. These “bad” gut microbes may then affect the activity of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis via the vagus nerve, which can affect crucial neuronal cellular activity in the brain and cause inflammation and neurodegeneration.
Everything from anxiety levels to heart rate to digestion to weight gain and much more can be affected by how well the vagus nerve is working and, consequently, how well the gut and the brain are communicating.
How to improve the Vagus nerve and boost overall health.
Fortunately, there are several things we can do on our own to enhance vagus nerve communication between the brain and the gut. The actions listed below can support healthy parasympathetic and sympathetic balance, regulate vagal tone, and lower inflammation (which can impair vagus nerve function). As a result, you may recover from stressful situations faster, have better digestion, and experience a variety of other all-encompassing advantages.
7 Diet Tips To Improve Vagus Nerve Health
1) Tryptophan
Tryptophan is metabolised in the gut and may help the astrocytes—cells in the brain and spinal cord—control inflammation, which may improve communication from the gut to the brain via the vagal messenger pathway. These foods include spinach, seeds, nuts, bananas, and poultry.
2) Reduce Sugar Intake
In addition to causing chronic inflammation, excessive sugar also damages cellular feedback loops and other signaling pathways. Inflammation of the mucosal lining of the GI tract also enables bacteria to continue sending inflammatory signals to the brain.
3) Probiotics
To promote gut health and preserve normal gut-brain transmission, reduce your sugar intake and think about incorporating fermented foods or a probiotic into your diet. The vagus nerve can actually be stimulated by intestinal microbes, according to research.
4) Fiber
Maintain regular sleep and activity schedules, eat a lot of fiber-rich foods each day (target for 25 grams or more), and consume lots of fiber-rich foods to help your body excrete on a daily basis. Healthy elimination prevents the stagnation of inflammatory food residues in the colon and creates an environment that is less welcoming to undesirable organisms that can interfere with brain-gut connection.
5) Less Animal Protein
Choline, which can be beneficial for you and is found in red meat and eggs, is transformed into trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), a substance linked to inflammation and cardiovascular problems, when ingested in excess. By consuming fewer of these items, inflammation may be reduced, and the vagus nerve will be better able to control sympathetic and parasympathetic vitals including blood pressure and heart rate.
6) Intermittent Fasting
According to some research, the vagus nerve can be stimulated by fasting and dietary restrictions. Fasting also has a number of other advantages, such as enhanced cognitive performance, weight loss, and decreased inflammation, so it might be worthwhile to give it a try. The best part: You don’t need to fast for a very lengthy period of time to benefit greatly.
7) Maintain a healthy weight
The relationship between the brain and the GI tract can be significantly impacted by obesity and gut inflammation, which can impair vagal activity. Therefore, if you are overweight, it is advisable to use long-term weight loss strategies that are sustainable. My recommendation is to engage in regular physical activity and concentrate on eating a diet rich in a variety of fruits and vegetables, as well as nuts, seeds, and legumes, like the Mediterranean diet.
Read More